
GBP categories are the #1 local ranking factor in Google’s algorithm. According to Whitespark’s 2023 Local Search Ranking Factors Survey, GBPs’ primary category is the number one local pack/finder ranking factor. Choosing the right primary and secondary categories can dramatically improve your local search visibility, but with over 3,794 available categories, strategic selection is crucial for success.
Selecting the wrong GBP categories is one of the fastest ways to sabotage your local search rankings. Every month, businesses lose potential customers because they’ve chosen generic categories instead of specific ones, or they’ve diluted their relevance by adding too many unrelated secondary options.
This comprehensive guide will show you exactly how to choose, optimize, and leverage GBP categories to dominate local search results. Whether you’re managing a single location or multiple business profiles, these data-driven strategies will help you outrank competitors and attract more qualified leads.
Key Takeaways
- Primary category is the #1 local ranking factor – invest time in strategic selection
- Specificity beats generality – choose the most specific accurate category available
- 3-5 secondary categories typically outperform 8-9 poorly chosen options
- Test and optimize category selections based on actual performance data
- Stay current with Google’s monthly category additions and changes
- Align categories with your most profitable services and business goals
- Monitor competitors to identify category opportunities and threats
What Are GBP Categories and Why They Matter for Local Rankings
GBP categories are classification labels that tell Google exactly what type of business you operate. Think of them as your business’s DNA in Google’s local search algorithm. When creating a Google My Business Listing, one of the first steps is to choose a business category. This consists of setting 1 primary category and up to 9 additional business categories. This is one of the biggest ranking factors in Local Pack.
These categories serve three critical functions for local businesses:
Search Matching: When someone searches for “Italian restaurant near me,” Google uses category data to determine which businesses should appear in results. Your business categories inform your customers about what your business does. It helps your business connect you with customers who search for your products or services.
Competitive Positioning: Categories determine which businesses you compete against in local pack results. A “pizza restaurant” competes differently than a generic “restaurant” in search results.
Feature Access: Specific categories unlock unique GBP features. Based on your business category, you might notice special features available for your Business Profile. Hotels: Can show class ratings and list the amenities it offers. Restaurants: Can add links for online orders, reservations, and menus.
The impact on rankings is undeniable. Businesses that optimize their category selection often see immediate improvements in local pack visibility, with some seeing 50%+ increases in direction clicks and profile views.
The Numbers Behind Category Impact
As of August 2nd, 2025, there are 3794 Google Business Profile categories, which are frequently updated by Google. In the last 30 days, 2 new categories were added (Probate Attorney, and Rv Repair And Maintenance Service Dealer). This constant evolution means businesses must stay current with category options to maintain competitive advantage.
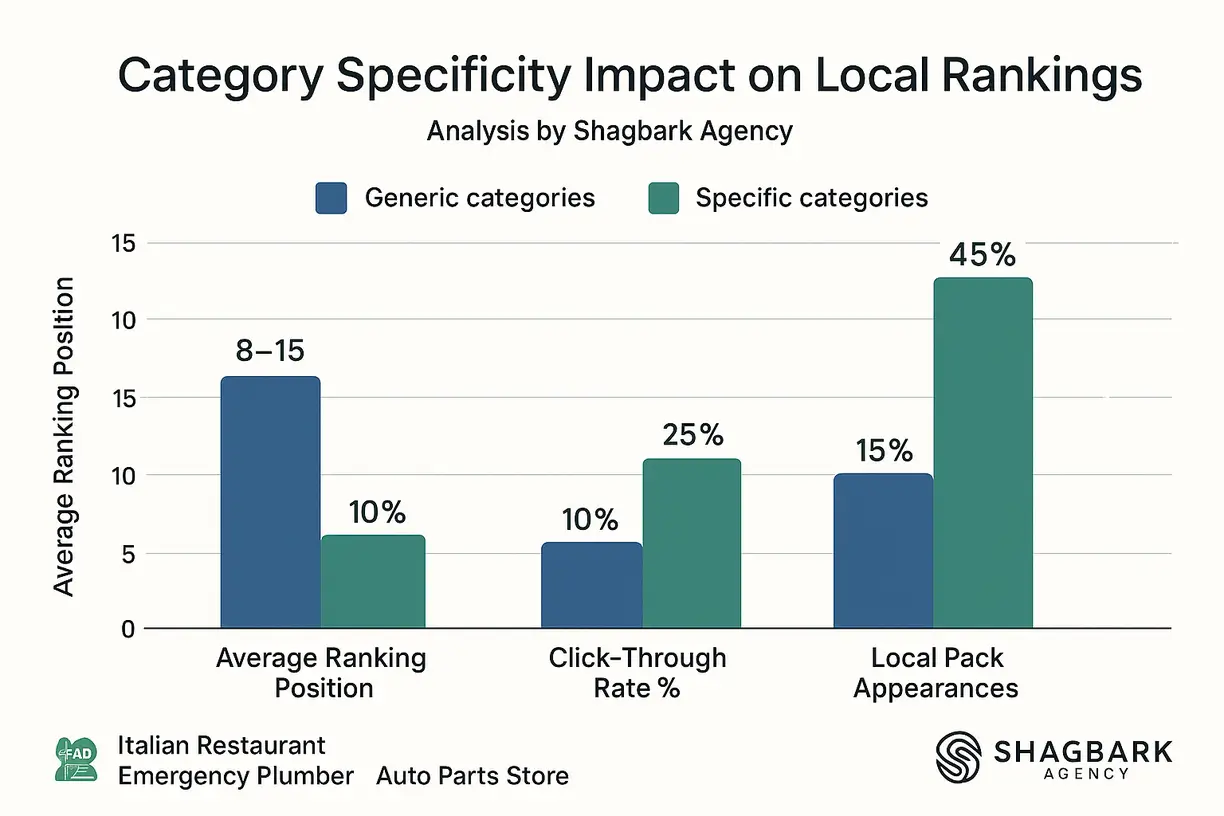
Research shows that businesses using specific categories consistently outrank those using generic alternatives. For example, “divorce attorney” typically outperforms “attorney” in relevant searches, even though both accurately describe the business.
Pro Tip: Monitor category additions monthly. Google frequently introduces highly specific categories that could give your business a competitive edge in niche markets.
Complete List of GBP Categories (2025 Updated)
Understanding the scope of available categories is essential for strategic selection. Google is adding/removing categories every month so you should keep a close look for new categories that describe you business better. The current category ecosystem includes everything from highly specific options like “Probate Attorney” to broad classifications like “Legal Services.”
Categories are organized across major industry verticals:
Professional Services: Accounting, legal, consulting, real estate, insurance, and financial services Healthcare: Medical practices, dental offices, veterinary clinics, wellness centers, and therapeutic services
Retail: Clothing stores, electronics shops, grocery stores, specialty retailers, and e-commerce pickup locations Food & Beverage: Restaurants by cuisine type, cafes, bars, catering services, and food trucks Home Services: Contractors, repair services, landscaping, cleaning, and maintenance providers Entertainment: Gyms, movie theaters, entertainment venues, recreation centers, and event spaces
The key insight is that Google favors specificity. Instead of choosing “restaurant,” select “Italian restaurant,” “pizza restaurant,” or “authentic Japanese restaurant” when applicable.
Industry-Specific Category Breakdowns
Different industries have varying levels of category granularity. Healthcare and legal services offer the most specific options, while some emerging business types may only have broad category choices available.
Legal Services Example:
- Generic: “Attorney” or “Law Firm”
- Specific: “Divorce Attorney,” “Personal Injury Attorney,” “Employment Attorney,” “Bankruptcy Attorney”
Restaurant Example:
- Generic: “Restaurant”
- Specific: “Italian Restaurant,” “Thai Restaurant,” “Steakhouse,” “Vegetarian Restaurant”
The primary category plays a significant role in rankings, so you want to pick the category that is the closest match with the most valuable term you want to rank for. In most cases, this will be the more specific category, rather than the broad category.
Pro Tip: Use competitor analysis tools to identify which specific categories are driving results in your market. Businesses often discover profitable niche categories they hadn’t considered.
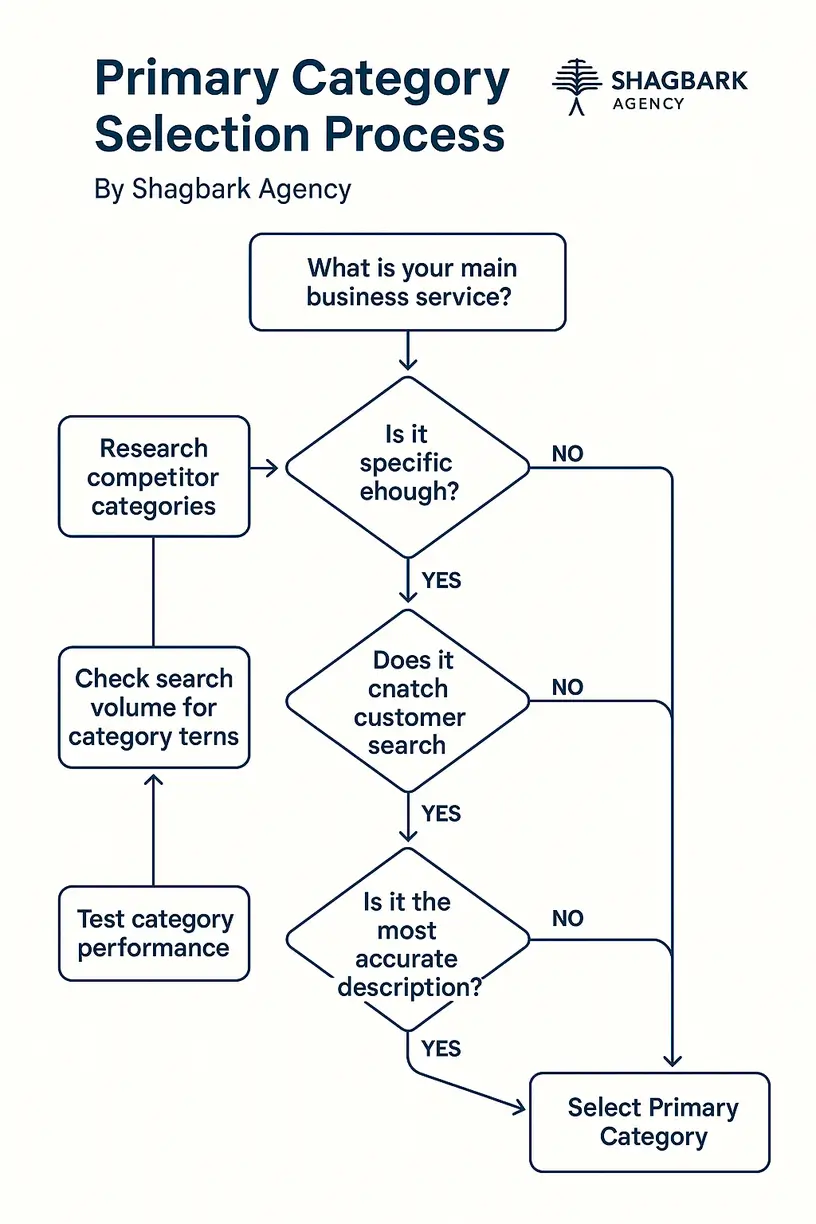
How to Choose Primary GBP Category: Strategic Decision Framework
Your primary category selection can make or break your local search performance. Your primary category is considered to be the single most important local ranking factor for a business in the local pack. Here’s a data-driven framework for making this critical decision:
The “This Business IS a…” Rule
You want your GBP categories to reflect the statement, “this business is a [insert category]” versus “this business has a [insert category]”. This simple test eliminates categories that describe features or amenities rather than core business identity.
Strategic Selection Criteria:
- Profitability Analysis: Choose categories that align with your highest-margin services
- Search Volume Research: Prioritize categories that potential customers actually search for
- Competition Assessment: Evaluate category competitiveness in your local market
- Business Goals Alignment: Select categories that support your growth objectives
Decision Matrix Approach:
For businesses that could fit multiple categories, create a scoring matrix:
- Revenue potential from category (1-10)
- Search volume for category terms (1-10)
- Local competition level (1-10, inverse scoring)
- Accuracy/relevance to core business (1-10)
The category with the highest total score typically becomes your primary selection.
Real-World Example: An HVAC business that offers heating, cooling, and plumbing services might score:
- “HVAC Contractor” (broad): Revenue 8, Volume 9, Competition 4, Accuracy 9 = 30
- “Heating Contractor” (specific): Revenue 9, Volume 7, Competition 7, Accuracy 8 = 31
Choose “Heating Contractor” if heating services drive more profit and face less competition.
When to Choose Specific vs. General Categories
When it isn’t so clear-cut, prioritizing the type of business you want to attract is a good rule of thumb. Ask yourself, what is most important moving forward?
Choose Specific Categories When:
- You specialize in a particular service or product type
- Specific categories have less local competition
- Your most profitable work comes from specialized services
- You want to attract qualified leads over volume
Choose General Categories When:
- You truly offer broad services across multiple areas
- Specific categories don’t adequately represent your business scope
- Local competition makes specific categories too difficult to rank for
- You’re in a market where customers search using general terms
Pro Tip: Test different primary categories over 60-90 day periods to measure impact on leads, calls, and direction requests. Real performance data trumps theoretical category selection.
How to Choose GBP Categories: Secondary Category Strategy
Secondary categories amplify your primary category’s impact and help you capture additional search opportunities. GBP allows for one primary category and up to nine secondary categories to be selected. You shouldn’t aim to fill in all nine secondary categories—choose only the ones that are most appropriate to your business.
Strategic Secondary Category Selection:
Complementary Services: Add categories for services that support your primary offering Geographic Variations: Include categories that might be searched differently in your area Business Evolution: Add categories for services you’re expanding into Seasonal Options: Consider categories that align with seasonal demand changes
Quality Over Quantity Principle:
Adding unrelated or barely related services can actually hurt your rankings by confusing Google. Stick to what your business actually does and does well. Three to five highly relevant secondary categories typically outperform nine loosely related ones.
Secondary Category Framework:
- Core Service Variations: Different ways customers might search for your main service
- Adjacent Services: Related services you provide that have their own categories
- Niche Specializations: Specialized aspects of your business that have specific categories
- Customer-Centric Categories: Categories that match how customers think about your business
Example for Family Law Practice:
- Primary: “Divorce Attorney”
- Secondary: “Family Law Attorney,” “Child Custody Attorney,” “Mediation Service,” “Legal Aid Office”
Secondary Category Selection Best Practices
Avoid Category Stuffing: Don’t add categories just because they’re available. Each category should represent genuine business activities.
Monitor Category Performance: Track which categories generate the most profile views, calls, and direction requests.
Update Seasonally: Some businesses benefit from seasonal category adjustments to match demand patterns.
Maintain Consistency: Ensure secondary categories don’t contradict or dilute your primary category’s message.
Pro Tip: Use Google Search Console data to identify which category-related keywords are already driving traffic to your website, then align your GBP categories accordingly.
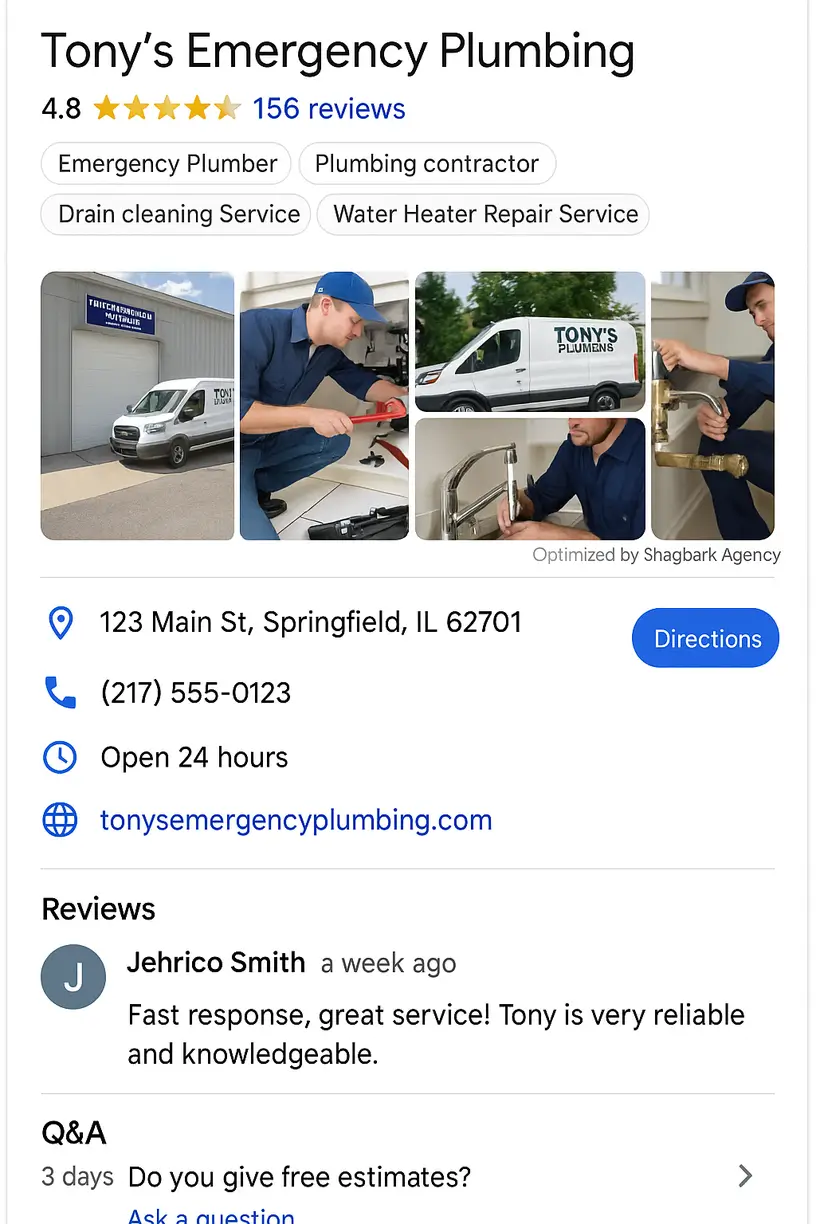
GBP Category Optimization Techniques That Drive Results
Beyond initial category selection, ongoing optimization strategies can significantly impact performance. Here are advanced techniques used by top-performing local businesses:
Seasonal Category Switching:
Adjusting the primary category to match seasonal demand allows these businesses to optimize their visibility for relevant searches year-round. If you’re in the HVAC industry, make sure to switch your GBP category from “air conditioning repair service” to “furnace repair service” at least a few weeks before the cold weather hits.
Industries That Benefit from Seasonal Switching:
- HVAC (heating vs. cooling focus)
- Landscaping (lawn care vs. snow removal)
- Event services (wedding vs. holiday planning)
- Retail (seasonal merchandise focus)
A/B Testing Category Combinations:
Systematic testing reveals which category combinations drive the best results:
- Baseline Period: Track current performance for 30 days
- Test Period: Change categories and monitor for 60 days
- Analysis Phase: Compare metrics including calls, directions, website visits
- Implementation: Adopt the winning combination permanently
Key Metrics to Monitor:
- Profile views and searches
- Phone calls and direction requests
- Website clicks from GBP
- Local pack ranking positions
- Customer acquisition cost from local search
Category Attribute Optimization:
You also want to consider the attributes associated with each category. Available attributes depend on the business category you select. Different categories unlock different business attributes, which can improve user experience and search visibility.
Advanced Category Research Methods:
Use competitor intelligence to inform category strategy:
- Analyze top-ranking competitors’ category selections
- Identify gaps in category coverage within your market
- Monitor new category additions that competitors adopt
- Track seasonal category changes in your industry
Advanced Category Testing Methods
Multi-Location Testing: If you have multiple locations, test different category strategies across locations to identify optimal approaches.
Keyword-Category Alignment: Ensure your website content and meta tags align with your chosen categories for maximum SEO impact.
Citation Consistency: Update categories across all major directories and platforms when you optimize your GBP categories.
Pro Tip: Create a category optimization calendar that outlines when to review and potentially adjust categories based on seasonal trends, business evolution, and competitive changes.

Common GBP Category Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
Even experienced business owners make critical category errors that limit their local search potential. Here are the most damaging mistakes and how to avoid them:
Mistake #1: Choosing Overly Broad Categories
Many businesses select general categories thinking they’ll capture more searches. Focus on accuracy, specificity and alignment with your most important services. Prioritize the category that brings you the work you want most. Instead of “contractor,” choose “plumbing contractor” or “electrical contractor.”
Mistake #2: Category Stuffing
Choose the fewest number of categories it takes to describe your overall core business. Adding every remotely related category confuses Google’s algorithm and dilutes your relevance signals.
Mistake #3: Mismatched Primary Category Selection
Choosing a primary category that doesn’t align with your most profitable or important services wastes your biggest ranking opportunity.
Mistake #4: Ignoring Category Updates
Google continuously adds, removes, and modifies categories. Businesses that don’t stay current miss opportunities to adopt more specific or advantageous category options.
Mistake #5: Inconsistent Category Usage
Using different categories across your GBP, website metadata, and other directories creates conflicting signals that can hurt rankings.
Category Selection Red Flags:
- Primary category doesn’t match your homepage title tag
- Secondary categories include services you don’t actually provide
- Categories haven’t been reviewed in over 12 months
- You’ve selected 8-9 secondary categories without strategic reasoning
Pro Tip: Conduct quarterly category audits to ensure your selections still align with business priorities, market conditions, and Google’s evolving category options.
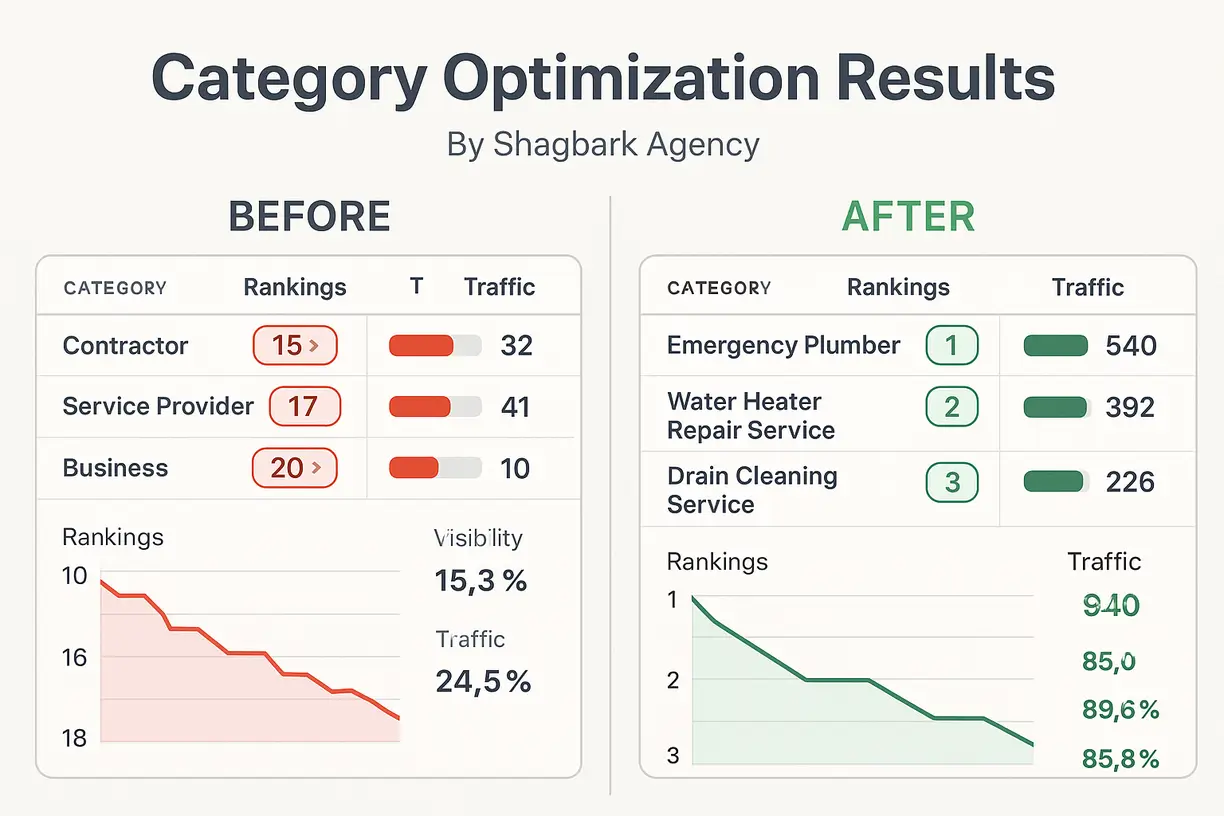
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Change Your GBP Categories
Updating your categories is straightforward, but strategic timing and implementation matter for maintaining rankings during transitions.
Access Your Category Settings:
- Sign in to Google Business Profile Manager
- Select your business location
- Click “Edit Profile” in the main dashboard
- Navigate to the “Business Category” section
- Click the pencil icon next to your current primary category
Category Update Process:
From the “Primary category” box, enter a category. From the list that shows up, select a category. Select Add another category. Enter a category. From the list that shows up, select a category.
Best Practices for Category Updates:
Timing Considerations: Make category changes during low-traffic periods to minimize disruption to visibility.
Verification Requirements: Some category changes may trigger re-verification requirements, particularly for sensitive industries like healthcare or finance.
Documentation: Keep records of category changes and performance impacts to inform future optimization decisions.
Monitoring Protocol: Track rankings and traffic for 30 days post-change to identify any negative impacts that need correction.
Technical Setup and Implementation
Category Change Checklist:
- Document current category performance metrics
- Research new category competition levels
- Update website metadata to align with new categories
- Prepare for potential verification requests
- Schedule follow-up performance review in 30 days
Rollback Plan: If category changes negatively impact performance, be prepared to revert to previous selections quickly.
Pro Tip: For businesses with multiple locations, test category changes on one location first to validate performance impact before applying changes across all profiles.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many GBP categories should I choose for optimal performance?
Choose one primary category and 3-5 highly relevant secondary categories. The best practice is to choose the most relevant category as your primary and to add 2-3 more additional categories that also describe your business but no more than 5-6 categories in total. Quality and relevance matter more than quantity.
Can I change my primary GBP category without losing rankings?
Yes, but changes should be strategic and well-timed. You are not stuck with the primary category you select. This can later be changed. Monitor performance closely for 30 days after changes to ensure positive impact.
How often should I review my GBP categories?
Review categories quarterly and monitor Google’s monthly updates for new relevant options. Google constantly changes, removes and adds new categories to GBP. Make sure to check monthly or quarterly for additional relevant categories you may want to add to your listing.
What’s the difference between how to choose primary GBP category vs. secondary categories?
Primary categories should represent your core business identity and most profitable services. Secondary categories can include complementary services, specializations, and alternative ways customers might search for your business.
How do I find the complete list of GBP categories for my industry?
There are 4274 Google business categories in total. Access updated lists through tools like PlePer or Sterling Sky, which track monthly category changes and additions.
Should I optimize GBP categories differently for multiple locations?
Yes, each location should have categories optimized for its specific market conditions, competition levels, and local search patterns while maintaining brand consistency.
Ready to Transform Your Local Search Performance?
Don’t let poor category selection keep your business invisible in local search results. GBP category optimization is just one piece of a comprehensive local SEO strategy that drives real business growth.
Our team has helped hundreds of businesses achieve dramatic improvements in local search visibility through strategic category optimization, complete profile optimization, and ongoing performance monitoring.
Get a free video SEO audit of your Google Business Profile and website to identify exactly what’s limiting your local search performance. We’ll analyze your current category selections, identify optimization opportunities, and provide a customized roadmap for dominating local search results.
Book Your Free Video SEO Audit – no obligations, just actionable insights that can immediately improve your GBP categories and local search rankings.
Transform your local search presence and start attracting more qualified customers today. Your competitors are already optimizing their GBP categories – don’t get left behind in local search results.
Check Our Other Important Guides:
Google Business Profile Category Optimization Guide
How to Recover Local SEO Rankings
Google Business Profile Posts Best Practices
Need Help with Local SEO Recovery?
If your local business has lost search rankings and needs expert recovery assistance, our team of Local SEO specialists is ready to help. Contact us for a free local SEO audit and recovery consultation.
Get Free Local SEO Audit
One thought on “GBP Categories: The Complete 2025 Guide to Google Business Profile Category Optimization”
Comments are closed.